How Diabetes Affects Eyes?
Diabetes is a disease that impairs your body’s ability to regulate blood sugar. Having diabetes increases your risk of developing serious vision problems including cataracts, glaucoma, diabetic retinopathy and double vision. For those with diabetes, regular eye exams are recommended with a retinal specialist to avoid vision impairment due to diabetes. Below is a list of potential diabetic related eye health disorders Retina Health Center specializes in treatment for:
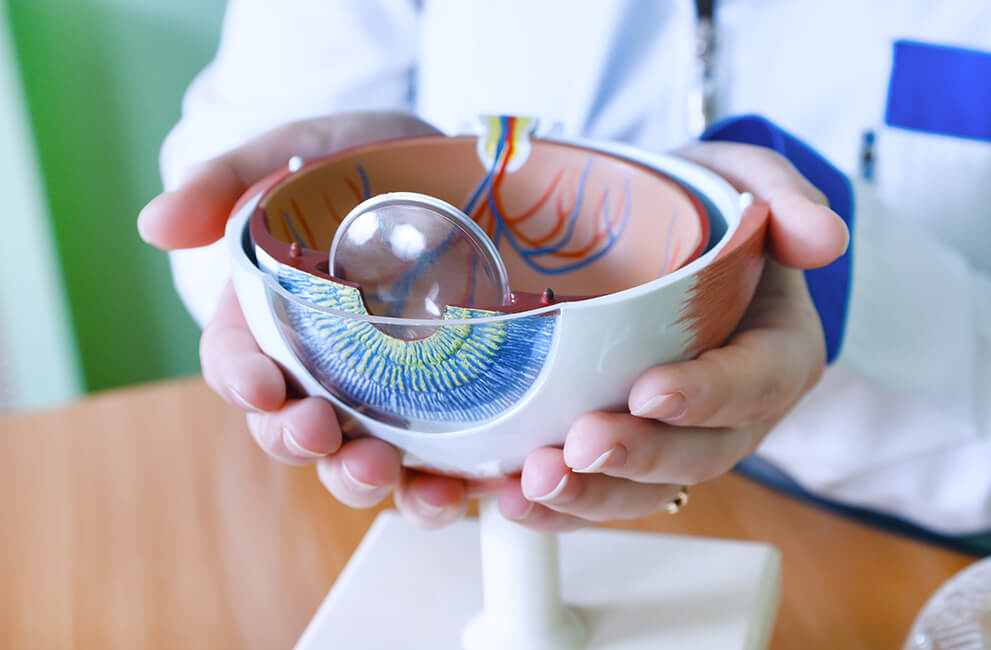
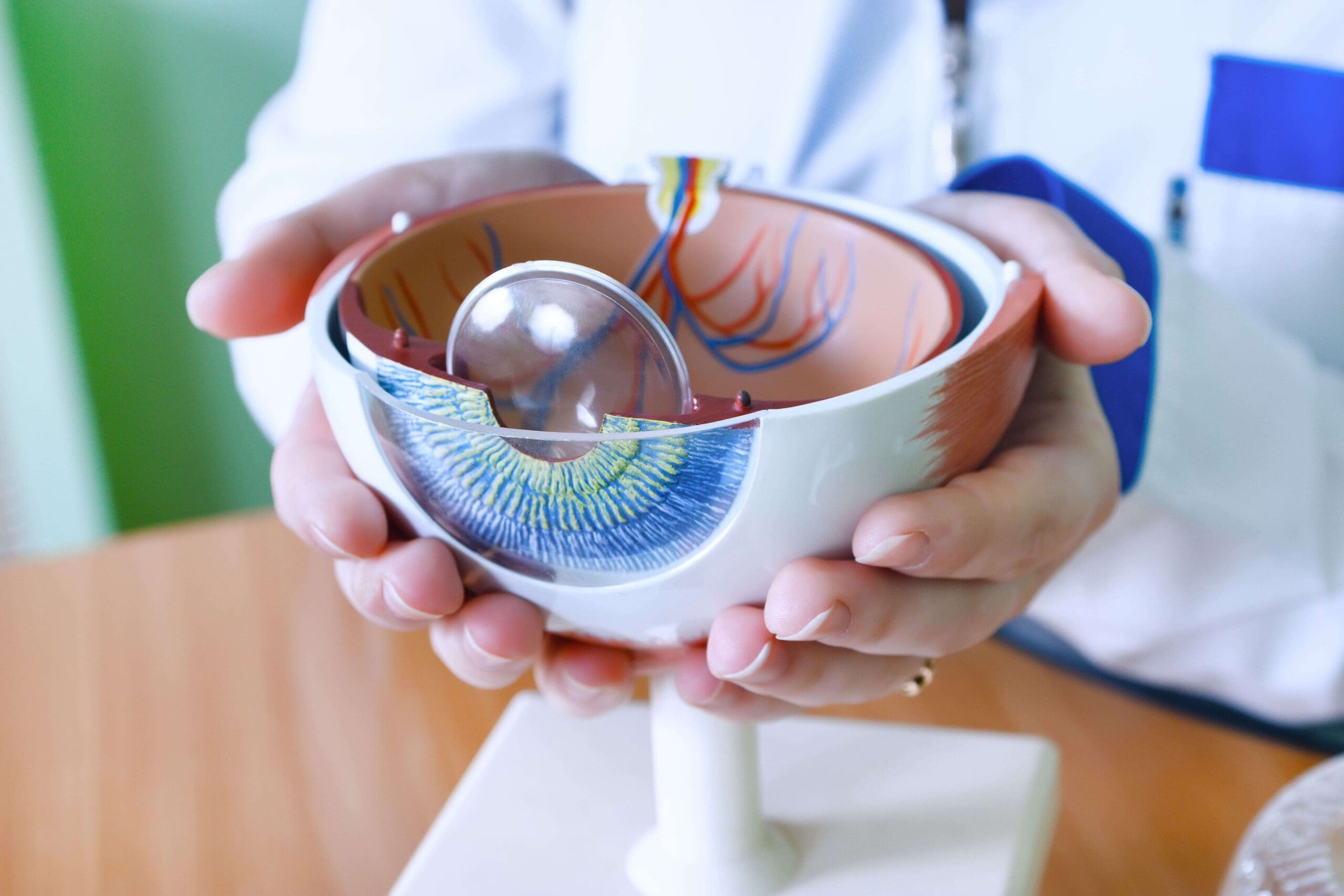
Diabetic Retinopathy
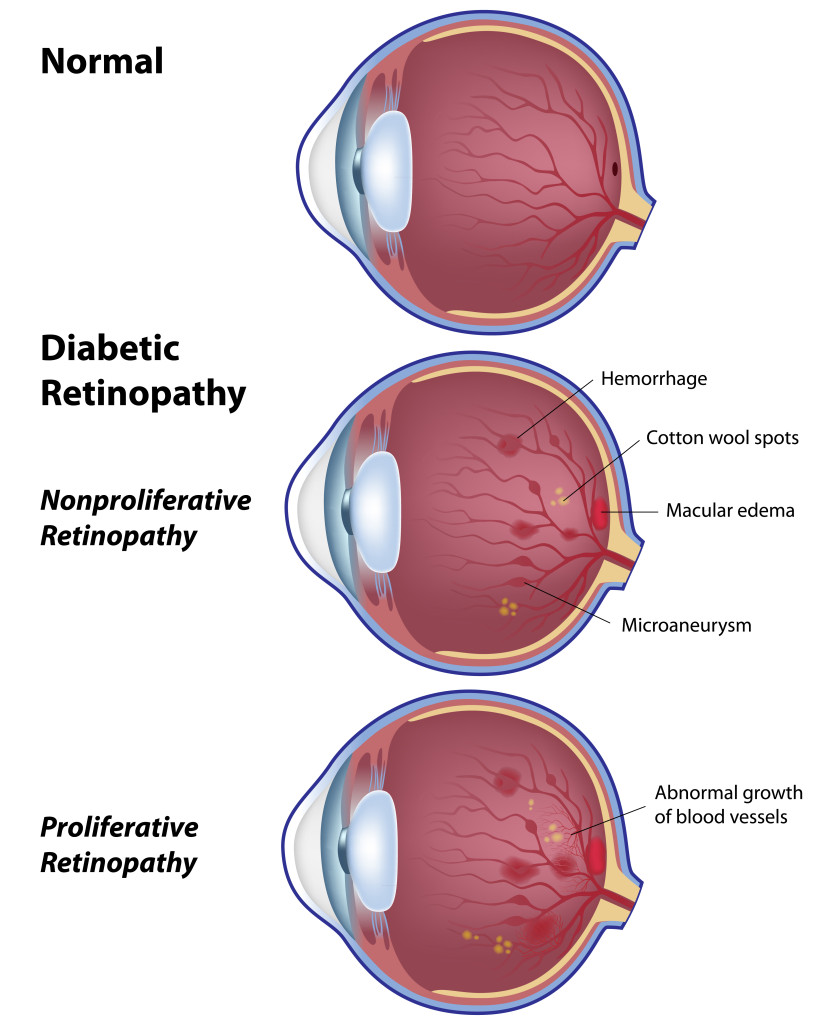
Diabetic retinopathy is the general term used for eye complications affecting the retina due to diabetes. It is described as the weakening of the blood vessels that supply blood to the retina. It is the leading cause of vision loss in adults from 20 to 64 years of age, and afflicts approximately 90 percent of patients who have had diabetes for 15 years or longer. Juvenile diabetics are especially prone to diabetic retinopathy at an early age. The condition may be aggravated by pregnancy or high blood pressure. Fortunately, most vision loss can be prevented through regular eye examinations and early treatment.
- Background diabetic retinopathy or non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy, is an early stage of the condition. Diabetic retinopathy involves changes in the blood vessels within the retina. Some shrink and others grow to form balloon-like sacs that may leak or hemorrhage. In the majority of cases, sight is not seriously affected. However, background retinopathy is a warning that sight may be endangered in the future, so more frequent eye exams are required to monitor further deterioration.
- Diabetic macular edema is a more serious form of diabetic retinopathy. Fluid accumulates in the macula, the center portion of the retina, and can cause distortion or even loss of central vision.
- Proliferative diabetic retinopathy is the most severe stage and the most threatening to sight. Caused by a lack of oxygen to the eye, the condition stimulates the abnormal growth of blood vessels.
These vessels are fragile and may rupture. Scar tissue from ruptured blood vessels may tighten and pull on the retina, detaching it from the inner wall. There is no pain, and partial loss of sight or even blindness may result.
Preventing Diabetic Retinopathy
The best way to prevent the development of diabetic retinopathy is to keep your blood sugar, cholesterol and blood pressure under control. Regular checkups with your medical doctor, exercise and a healthy diet are also important.
Successful treatment of diabetic eye conditions depends greatly on your willingness to participate fully in your care. Regular eye exams are critical to maintaining vision. It is much easier to prevent vision loss from diabetes than to restore sight after it is lost.
If you notice a reduction in vision or an increase in the number of new floaters (the small specks or cobwebby stands that move into your field of vision) schedule an evaluation at Retina Health Center immediately.
Evaluation of Diabetic Eye Conditions
Routine eye exams are a vital part of preventing vision loss from diabetes. Diabetics under the age of 30 should have annual exams starting no later than five years after diabetes is diagnosed. Yearly eye exams are recommended for diabetics over the age of 30. If there is evidence of damage to your eye, however, more frequent exams may be necessary. Pregnant women should see their eye doctors at least once during the first three months of pregnancy.
At the Retina Health Center, specialized equipment is used to examine your eyes. If there is evidence of diabetic retinopathy, a fluorescein angiogram may be required. During this test, a fluorescent dye is injected into the bloodstream, and photographs of the retina’s blood vessel system are taken. These are used to evaluate the condition of the vessels and serve as a “road map” for laser treatment when laser treatment is needed. Another test that is frequently used is Ocular Coherence tomography (OCT), which creates a cross sectional image of your retina. This test will determine if there is swelling in your retina that may benefit from treatment.
Treatment of Diabetic Eye Conditions
While consistent control of blood glucose levels and hypertension are necessary to preventing the progression of the disease, if treatment is recommended for diabetic retinopathy, several options are available with the Retina Health Center.Laser Surgery
If diabetic retinopathy is detected early, in-office laser treatment is typically used to arrest damage. Patients would visit the Retina Health Center offices in Fort Myers or Naples, where the procedure would be performed. To reduce leaking in blood vessels for patients with diabetic macular edema, a laser is used to seal the leaky blood vessels. Laser treatment is also used to halt abnormal blood vessel growth for patients with proliferative diabetic retinopathy.
Vitrectomy
In severe cases of proliferative diabetic retinopathy, bleeding occurs in the vitreous, the gel-like substance in the center of the eye. In some instances it clears naturally and no further treatment is necessary. However, if it does not clear, a vitrectomy – surgical removal of the cloudy material – may be advised.
Other treatments
In addition to laser and surgery, a number of medications are now available to treat diabetic retinopathy. These include Lucentis, Eylea, Ozurdex, and the long acting ILUVIEN implant. Additionally, Avastin and/or Triamcinolone may be used in an off label fashion to treat advanced diabetic retinopathy, and can restore vision is some patients. If it looks like these medications will help, your doctor will discuss them further with you.














